
Fundamentals Followed by UX Designers
Fundamentals Followed by UX Designers
Well, we have already discussed what a UX designer is and what the roles and responsibilities of a UX designer are in our previous blogs. In this article, we will discuss the fundamentals to be followed by a UX designer while designing. How should they focus on each aspect carefully and keep stakeholders happy?
Importance of UX Design in Modern Applications
User experience is a critical factor in the success of digital products. A well-designed UX ensures user satisfaction, leading to better engagement and higher conversion rates. Whether you’re building a website or a mobile application, investing in a strong UI/UX Design Service can make a significant difference in user retention and overall business success.
Aligning UX Disciplines
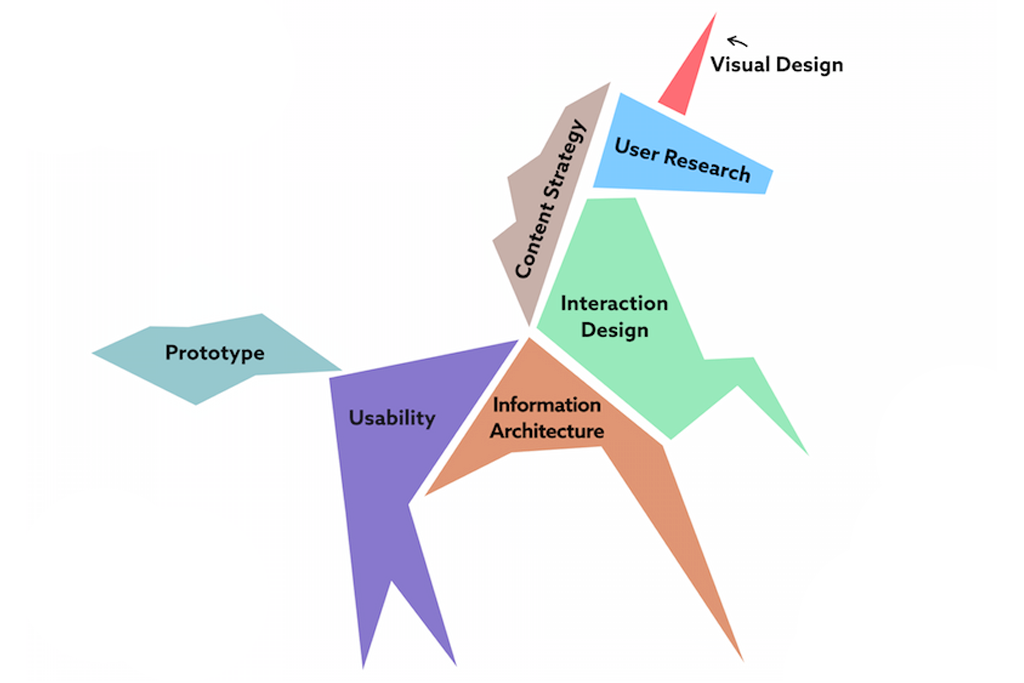
After thorough research and analysis, I have aligned eight fragments to form a UX design process unicorn, which my team helped me describe. This is how we function to achieve results.
Essential Parts of UX
Interaction Design
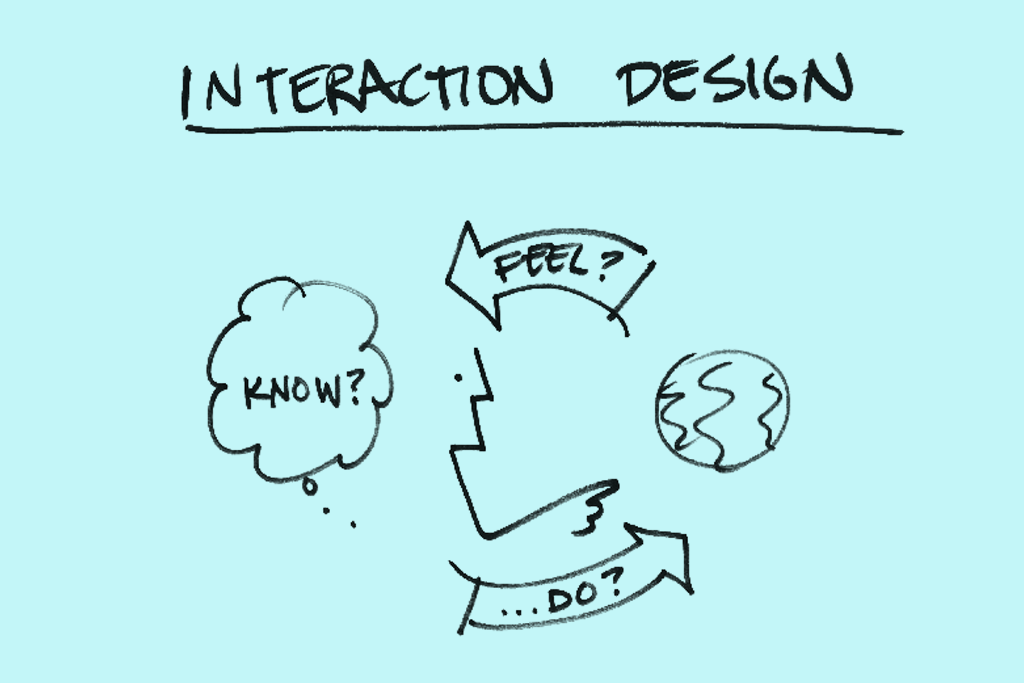
This stage examines the interaction between the system and its users. It focuses on developing an outline and how to present information so that users can understand the information in the best way.
“Every great design begins with an even better story.” — Lorinda Mamo, Designer / Creative Director
Though interaction design is a subset of UX design, every UX designer is not competent in interaction design. Ever since the dawn of computing, it has become imperative to interact with our products. Thus, the simpler you keep the interaction, the more beautiful it is.
Visual Design

Based on initial design theories developed by interaction designers, visual designers work by applying typographical hierarchy, color, material patterns, and iconography. To formulate the overall visual appeal of product designers, they try to establish micro-interactions to fit together.
“Like all forms of design, visual design is about problem-solving, not about personal preference or unsupported opinion.” — Bob Baxley
Usability
At this stage, the experts investigate product pathways for the suitability of users. They try to identify the errors via testing and check that users do not get confused. They then give necessary instructions to the team for required adjustments. Essential testing helps in finding future ideation and revising product influence.
“Usability is about people and how they understand and use things, not about technology.” — Steve Krug
The major focus in this stage is on whether our product is easy to use and whether users/customers will use our product.
Tools in Use: Test plans, proof of concept, testing debriefs, guerrilla testing, A/B testing.
Information Architecture
A UX architect examines the complete content before presenting it to users. Based on the user’s conceptual model, a content hierarchy is prepared. A thorough examination of the user’s thought process and behaviors is conducted. The major concern is on the content searched by users and what measures to implement for achievement.
Tools: Cluster group information, content hierarchy, sitemaps, card sorting.
Content Strategy
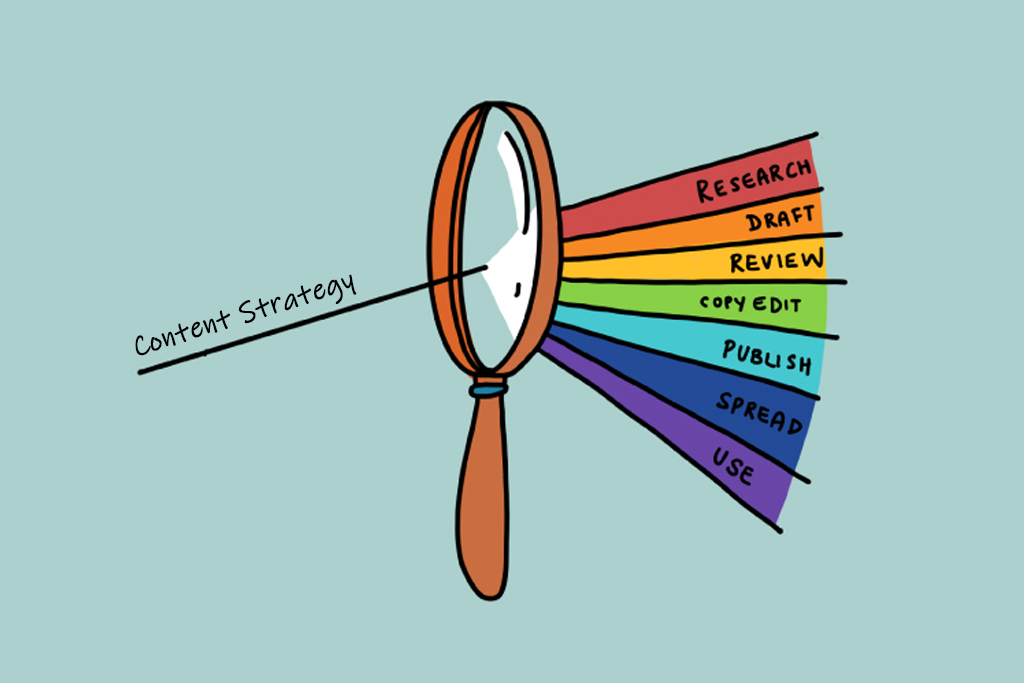
The work of content strategists is to analyze the user’s language and understand the intended meaning of users. They analyze and decide on content creation, the time of publishing, and exposure to users. While addressing users in various situations, a content strategist sets the voice of a product and tone. Thus, at this stage, the major focus is on effective communication with users.
“UI is the saddle, the stirrups, & the reins. UX is the feeling you get being able to ride the horse.” — Dain Miller, Web Developer
Tools Required: Content guidelines, tone decisions, modeling, and product voice.
User Research
UX researchers examine the behaviors, activities, obligations, needs, and environment of users. They observe and identify (internal and external) user struggles and provide potential solutions to the team. The team of researchers works on a holistic approach where they incorporate the concept of user existence and not just the product.
The team focuses on examining a user’s existence, environment, and behavior.
Tools Required: User interviews, analytical statistics, process life cycle, user journey mapping, workshop personas, and user surveys.
Prototyping
Prototypers draft versions of the product as part of their responsibility. Prototypes are also known as UXers, data scientists, or engineers. Their work is to create a variety of workflows—coded and non-coded—to provide concept proof. Creativity is the key focus at the prototyping stage.
“Creativity is allowing yourself to make mistakes. Design is knowing which ones to keep.” — Scott Adams
While prototyping, design ideas are captured, interactivity is tested, and an effective problem-solving strategy is designed.
Tools Required: Interactive animations, HTML/CSS/JavaScript, clickable workflows.
Conclusion
Measure your company’s UX maturity before growing your team. UX designer fundamentals are essential elements in the design process. At GKMIT, we build step-by-step procedures for achieving the perfect UX team output. We take baby steps for smart growth, focusing on diversifying knowledge and increasing team efficiency through constant updates. Figure out gaps in your UX process story with our expert guidance.
Energize your UX with the above disciplines.
Yay… I hope you found our blog helpful!